





Ayushman Bharat
Mission Indradhanush
Maternal and Neonatal
Tetanus Elimination (MNTE)New Vaccines
Pradhan Mantri National
Dialysis Program (PM-NDP)Pradhan Mantri Surakshit
Matritva Abhiyan (PMSMA)Affordable Medicines and Reliable
Implants for Treatment (AMRIT)Free Drugs & Diagnostic Services Initiative
Rashtriya Bal Swasthya Karyakram (RBSK)
Mission Parivar Vikas (MPV)
Budget Allocation
National Health Mission (NHM)
National Urban Health Mission (NUHM)
Major Policy Initiatives
Tertiary Health And Medical Education
National Programs
National Vector-Borne Disease Control Programme
National Mental Health Programme (NMHP)
Food Regulation - Food Safety and
Standards Authority of India (FSSAI)Drug Regulation
IT Initiatives
Mobile Applications
Development of Inter-Operable Electronic Health Records (EHR) System
Telemedicine




Launched with two pillars:
I.
Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Swasthya Suraksha Mission (PMRSSM) -
the largest publicly funded health protection scheme of the world.
Health insurance to over
10 crore underprivliaged and vulnerable families
(approx. 50 crore people)
Coverage up to
Rs. 5 lakhs/family/year
to protect the poorest from catastrophic healthcare spending
More than 40%
population to benefit


Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Swasthya Suraksha Mission (PMRSSM)
Salient Features

Cashless and paperless
access to services for the
beneficiary at the point of service in any (both public
and private) empanelled hospital across India.

No family size limit,
ensuring all family members,
specifically the girl child and senior citizens, get
coverage. It is suggested to
preferably make the
women as the head of the family.

I. Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Swasthya Suraksha Mission (PMRSSM)
Salient Features

The scheme is entitlement based. Every family figuring in defined SECC database will be entitled to claim
benefit under the scheme.
The beneficiaries will be encouraged to bring Aadhaar for the purpose of identification but no person will be denied benefits in the absence of Aadhaar.

A well-defined Complaint and Public Grievance Redressal Mechanism with robust safeguards to prevent misuse/ fraud/ abuse by providers and users.
Pre-authorisation
will be made mandatory for all tertiary care and selected secondary care packages.

II. Pradhan Mantri Health & Wellness Centres (PMHWC)

1.5 lakh
Sub Centres & Primary Health Centres
being transformed to HWCs

Will provide
Comprehensive Primary
Healthcare services

Services being provided
close to homes/community


Launched in December 2014 to achieve full immunization
coverage of at least
90% by 2020.
Under Intensified Mission
Indradhanush (IMI), this date has been advanced to 2018.

The completed four phases
of MI have covered
528 districts.

3.15 crore
children vaccinated

80.63 lakh
pregnant women immunized

79.73 lakh
ORS packets distributed

80.58 lakh
children fully immunized

91.94 lakh
Vitamin A doses administered

2.73 crore
zinc tablets distributed

Rate of annual increase in
coverage of full immunization
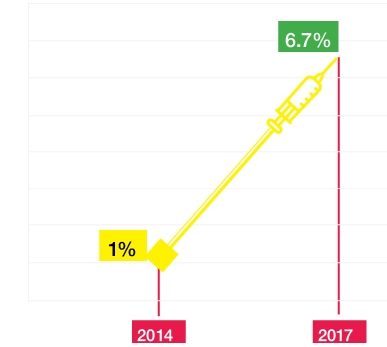
The first two phases of
Mission Indradhanush have led to an
increase of 6.7%
in full immunization coverage in one year.
As per the report of Integrated Child Health & Immunization Survey (INCHIS)


Intensified Mission Indradhanush
Launched by Hon’ble Prime Minister in October 2017
Implemented in identified and
121
districts
17
urban areas
52
districts
of NE states
(total 190 districts/urban areas across 24 states)


Biggest public health
milestone after India
being certified polio-free


Validation in India completed
in May 2015,
well before
the global target date
of
December 2015

5 new vaccines
have been added to India’s Universal Immunization
Program (UIP), bringing the
total to 12

Measles-Rubella (MR) vaccine:
Around
7.7 crore children
vaccinated

Pneumococcal Vaccine (PCV):
More than
14 lakh doses
administered

Rotavirus vaccine (RVV):
Nearly
1.42 crore doses
administered
Inactivated Polio Vaccine (IPV):
Nearly
3.87 crore doses
administered

Japanese Encephalitis vaccination in India:
Around
16 crore children
aged
1-15 years vaccinated

Adult JE campaign
covered around
3.29 crore adults

Free dialysis services for the poor and subsidized services
to all patients

497 operational
dialysis
units/centers
More than
22.84 lakhs
dialysis
session held
More than
2.38 lakh
patients
benefitted
Started with 219 districts in
2016 across the country, now
expanded to cover
356
districts
6
dialysis machines in
every facility - will be
extended up-to 10 machines
3,330
operational
dialysis
machines


Aims to provide special assured, quality antenatal care, free of
charge universally to all pregnant women on the 9 th of each month in
partnership with private sector doctors.


More than
1.25 crore
ANCs
conducted


More than
6 lakh
high-risk
pregnancies
identified


Conducted at over
12900 health
facilities across all State/UTs

Over
4900 volunteers
registered on PMSMA portal across all State/UTs


To provide drugs for cancer, cardiovascular diseases including cardiac
implants
implants at
60 to 90%
discount on prevailing market rates.

134 AMRIT
Pharmacies
across 22 States, selling
more than 5200 drugs
(including cardiovascular, cancer, diabetes, stents, etc), implants, surgical disposables and other consumables

More than
67.29 lakh patients
benefitted


The value of drugs dispensed at MRP Rs. 629.19 crores, resulting in
savings of Rs. 346.59 crores


All states/UTs have notified policy to provide free essential drugs
29 States
are implementing IT backed drug logistics system

Total support given to States/ UTs
under NHM during 2014-18 is
Rs. 13918.99 crores
(both cash and kind)

Free Drugs Initiative
Salient features

Facility wise
Essential
Drug List
(EDL)

IT backed
logistics &
supply chain
management

Robust
procurement
system

Standard
treatment
guidelines

Proper
warehousing
including
necessary
drug
regulatory
and quality
assurance
mechanisms

Prescription
audit

Grievance
redressal
systems etc.

Free Diagnostics Initiatives
Aims to reduce out-of-pocket expenditure on
diagnostics and improve quality of care


States supported to provide essential diagnostics free of cost in public health facilities


Point of care diagnostic to be made available in the Health and Wellness Centres (HWC)

Budgetary provisions made for diagnostics at HWCs


Aims at early identification and intervention for children from birth to 18 years to
cover 4Ds: Defects at Birth, Diseases, Deficiencies and Development Delays

Free management of 30 identified health conditions including surgery at tertiary health facilities
Around
70.9 Crore
children screened and
1.55 Crore
children have received treatment till September 2017


Launched in July 2016 in
146 high fertility districts
of 7 states-
Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand and Assam


New contraceptives
made available till the Sub-Centre Level

Saas Bahu Sammelan:
Encouraging young married women and their mothers-in-law to freely discuss matters related to family planning and reproductive health

Nayi Pehel:
Family planning kit for newlyweds made available with ASHAs

Saarthi:
Family Planning mobile van offering information and services at the community’s doorstep

Unprecedented
increase of 11.5%
in the outlay of health in 2018-19 over 2017-18
Allocation of 2017-18 was Rs.47,352.51 crore and
2018-19 is Rs.52,800 crore
Rs. 24,908.62 crore provided for NHM in 2018-19,
Rs. 2967.91 crore more
than last year
Human Resource & Medical Education
Rs. 200 crore allocated



Aims to strengthen health systems across the country

Strengthening Infrastructure
Completed:
7990
constructions and
9615
renovations

8149
AYUSH doctors engaged

Sanctioned:
4814
new constructions and
7557
renovations of health facilities including SC, PHC, CHC, SDH and DH

73879
ASHAs selected across the country and
76283
health kits provided

4 Crore Village
Health and Nutrition Days (VHND) held

Operationalized
3659 vehicles
supporting
Dial 102/104
services
2230 vehicles
supporting
Dial 108
services


Biomedical Equipment Maintenance and Management Program (BMMP)
Aims to ensure maintenance of medical devices in the public health facilities (up to
District Hospitals) to enable delivery of good quality diagnostics and therapeutic care

To maintain a functional state of medical devices
24x7, 365 days
with an uptime of 95% for all medical equipment in District Hospitals, 90% for SDH/CHCs and 80% for PHCs.

Inventory mapping of all biomedical equipment completed in
29 States/UTs.

Contact agreement for maintaining medical devices is given to service providers selected via open tender in 16 States/UTs and maintained in-house by 4 States/UT.


National Ambulance Services
Referral transport services provided through
Dial 108/102
ambulance services
As of December 2017,
24276
ambulances were operational


National Mobile Medical Units (MMU)
The objective is to take health care to the doorstep of the public in the rural and underserved areas
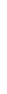
1416
MMU operational in the country across
408
districts

Approved in May 2013 to strengthen primary health care services in urban areas with special focus on slum dwellers and vulnerable population


Covers cities/ towns with more than
50,000
population, district headquarters and State headquarters with more than
30,000
population

Presently implemented in more than
1000
cities/towns



National Health Policy 2017
National Health Policy 2017 formulated after a gap of 15 years - to address the current and emerging challenges since the last National Health Policy was framed in 2002.



Assured affordable health services for all

Health allocation to be increased to 2.5% of GDP

‘Make in India’ for affordable healthcare

Free drugs, diagnostics, emergency and essential services for all

Focus on preventive and promotive healthcare

Improvement in hospital facilities by periodic quality checks

All families to get a health card

Time-bound action for control of diseases

Effective grievance redressal mechanism

HIV & AIDS (Prevention & Control) Act, 2017

Aims to end the epidemic by 2030 in accordance with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).

A person living with AIDS cannot be treated unfairly at employment, educational establishments, renting a property, standing for public or private office or providing healthcare and insurance services.

Every HIV infected or affected person below the age of 18 years has the right to reside in a shared household and enjoy the facilities

Prohibits any individual from publishing information or advocating feelings of hatred against HIV positive persons and those living with them
Every person in the care and custody of the State shall have right to HIV prevention, testing, treatment and counselling services

Suggests that cases relating to HIV positive persons shall be ‘disposed off’ by the court on a priority basis and duly ensure the confidentiality
No person shall be compelled to disclose his/her HIV status except with their informed consent, and if required by a court order

Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana (PMSSY)
Aims at correcting regional imbalances in the availability of affordable/reliable tertiary healthcare services and also augmenting facilities for quality medical education in the country.

Cabinet has approved
8
new AIIMS at

Mangalagiri (Andhra Pradesh)

Nagpur (Maharashtra)

Kalyani (West Bengal)

Gorakhpur (Uttar Pradesh)

Bathinda (Punjab)

Guwahati (Assam)

Bilaspur (Himachal Pradesh)

Deoghar (Jharkhand)

Medical Education
A uniform entrance examination for admission to all medical seats in the country viz. National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (NEET) has been introduced by amending the Indian Medical Council Act, 1956.

For the first time, common counselling for entrance to all medical seats has also been made mandatory by amending the Regulations in 2017.
Total 92 Medical College (46 Govt. and 46 Pvt.) established in last four years, resulting in an increase of 15354 MBBS seats (6519 in Govt. Colleges and 8835 in Pvt. Colleges).
Total 12646 PG Seats (Broad & Super Specialty Course) increased

DNB seats increased by around 2000
In the first Phase, in 72 Government Medical Colleges, approx. 1500 PG seats created.
Against a target of 58, 57 proposals have been approved till date and 8 colleges have become

For ensuring the availability of one medical college in every 3 Parliamentary Constituencies and one
Government Medical College in each State, 24 more new medical college will be established in 8 unserved/underserved States.
2400 new MBBS seats will be created

National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer,
Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases & Stroke (NPCDCS)
36
State NCD cells
established
439
District NCD cells
established
482
District NCD Clinics and
2349
NCD Clinics at CHC set up
155
Cardiac Care Units (CCU),
84
District Day Care Centers set up

National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer,
Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases & Stroke (NPCDCS)
More than
3
crore persons
screened at NCD Clinics
till March 2018
Population-based
screening for prevention
and control for common
NCDs in more than
150
districts and more
than
70
lakh people
screened till date

National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer,
Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases & Stroke (NPCDCS)
National Cancer Institute being set up
at Jhajjar at Haryana.
34
State Cancer Institute/Tertiary Care
Cancer Centers approved to monitor
all Cancer-related activities of their
respective areas
The second Campus of Chhitaranjan
National Cancer Institute being set up
in Kolkata

Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme (RNTCP)

Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme (RNTCP)

Treatment for drug-sensitive TB is provided through a network of more than
4 lakh
DOT Centres


14781
Designated Microscopy Centres established for the quality diagnosis of TB


House to house screening of TB symptoms has covered
5.5
crore population as part of Active Case Finding (ACF) in 2017 in
3
phases of 15 days each.

Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme (RNTCP)

1135
CBNAAT machines are installed. All District Hospitals and Medical Colleges have CBNAAT Machines


Rs. 500
per month for nutritional support to all TB patients for the entire duration of TB treatment through DBT


Rs. 1000
for notification and outcome reporting for Private providers /Chemists /laboratories

National AIDS Control Program (NACP)

National AIDS Control Program (NACP)

National AIDS Control
Programme now a
100%
Central Sector Scheme

‘Test and Treat’ Policy
launched
for covering all
patients with Anti Retro Viral
(ARV) irrespective of CD4 count
or clinical stage

More than 1 lakh
additional
HIV infected people brought under
the ambit of ARV treatment in 8
months since the launch of ‘Test
and Treat’ policy

More than 11.75 lakh
people infected with HIV are on
ARV treatment, 54% higher than
March 2014

Viral Load Testing for all People Living with HIV/AIDS (PLHIV) launched, providing
free-of-cost viral load testing
at least once a year for around 12 lakh PLHIV on treatment

Anti-TB drugs
through
Single Window Services for TBHIV
co-infected patients at all
537 ART centres

More than 2 Crore
pregnant women being tested
for HIV in a year with a goal to
achieve elimination of Motherto-
Child Transmission of HIV
by 2020

National Tobacco Control Programme

Reduction in prevalence of tobacco use:
As per findings of Global Adult Tobacco Survey (2016-17), the prevalence of tobacco use has reduced by six percentage points from 34.6% to 28.6% during the period 2009-10 to 2016-17. The number of tobacco users has reduced by about 81 lakh.


Packaging and Labelling Rules:
Size of specified health warnings on tobacco products enhanced w.e.f. 1st April 2016 to 85% of the principal display area of tobacco product packs. The Quit-Line call centre number has been included in new specified health warnings.


The inclusion of Bidi in Tax Net:
Bidi
has been covered in the tax net and
kept along with all tobacco products in
the slab of 28% under the Goods and
Service Tax (GST).


WHO Director-General’s Special Recognition
Award:
Shri Jagat Prakash Nadda, Union
Minister of Health and Family Welfare have
been awarded the WHO Director-General’s
Special Recognition Award in 2017 for global
tobacco control.

National Organ Transplant Program

Organ Donation Rate (number of deceased organ donors per million population) has increased by four times since 2012-13.
Five Regional Organ and Tissue Transplant Organizations (ROTTO) established in Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, Assam, West Bengal and Chandigarh UT.

National Registry to provide an online system for procurement and distribution of organs and tissues established.
Policy and criteria for allocation of various vital organs approved and uploaded on NOTTO website.


Malaria
40 million LLINs
distributed in the
NE States, Odisha,
Chhattisgarh & Jharkhand


During 2015-17, reported
positive cases of
Malaria reduced by 28%,
and reported deaths due to malaria
reduced by 73 %.


Dengue & Chikungunya

Diagnostic facilities
increased
from 394 in 2013 to
618 in 2018



Case Fatality Rate (CFR) for
Dengue (deaths per 100 cases)
was
sustained at 0.2%
in last three years


Japanese Encephalitis (JE) / Acute Encephalitis
Syndrome (AES)
Sentinel sites increased
from 51 (2005) to
135
(2017)
Establishment of
Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU) in priority districts

Apex Referral Laboratories
increased
from 12 to
15
Establishment of Physical
Medicine Rehabilitation (PMR)
in identified Medical Colleges

State to notify any breakout/case of Japanese Encephalitis


Kala-azar (KA)
Reduction of 37.7%
in cases
from 9241 (2014) to 5758 (2017)

Single dose single day drug (Ambisome) introduced
in the programme in 2014.

Reported
deaths reduced by
100%,
from 11 (2014) to zero (2017)


Lymphatic Filariasis (LF)

Out of 21 endemic states/ UTs,
5 have achieved LF elimination target
and are under Post-MDA Surveillance.

Transmission Assessment Survey (TAS) cleared districts
increased from 5 (2014) to 97 (2017).

Enactment of the Mental
Healthcare Act, 2017
Expansion of the District Mental
Health Programme to
517
districts of the country.

Support for the establishment
of
14
additional Centres of
Excellence and strengthening/
establishment of
20
additional
Post Graduate Departments in
mental health specialities.




Globally benchmarked food standards:
500 food standards developed, reviewed and expanded for food additives that now has over
9000
provisions covering
350
additives and food processing aids.
Credible and robust food testing system:
A network of over
240 laboratories,
of which
169
are NABL accredited. Also provide Mobile Food Testing labs to States /UTs. IT-based Indian Food Lab Network (InFoLNet) developed for a seamless flow of information relating to food testing processing aids.


Fair and Transparent enforcement and hassle-free food imports:
Food Safety and Standards (Import) Regulations,
2017
notified. For ease of doing
business, Food Import Clearance System (FICS) integrated with ICEGATE system of
Customs under Single Window Clearance Interface to Facilitate Trade (SWIFT) at Delhi,
Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, Cochin and Tuticorin covering


Large-scale food fortification:
Standards formulated for fortification of key food staples viz. edible oil, double fortified salt, milk, wheat flour and rice. Logo launched to identify fortified foods. Food Fortification Resource Centre established to promote food fortification.
Food Recovery andFood Sharing:
An alliance of food recovery agencies developed to collect and distribute food to the
needy covering 70 cities.



Organ Donation Rate (number of deceased organ donors per million population) has increased by four times since 2012-13.

344 irrational fixed-dose
combinations (FDCs) prohibited.


New National List of Essential Medicines (NLEM, 2015) finalized.
376 medicines
now included.

Coronary stents
added in NLEM, 2015 and their ceiling prices fixed.



Commencement of online clearance of imports consignment through an integrated declaration
at a single entry point
i.e. the Customs Gateway (ICEGATE) with risk-based inspection and sampling.

The level of ‘Not of Standard Quality’ drugs in the country is as low as
3.16%
and spurious drugs even lower at
0.0245%
as per the largest ever survey in the world.

National Regulatory Authority (NRA) declared functional with the
highest maturity level of 4
in respect of 5 functions and 3 in respect of 4 functions.


National Health Portal (NHP)

National Health Portal (NHP)
provided health-related information to citizens and stakeholders in different languages (currently six languages). A voice portal provides information through a toll-free number
1800-180-1104
and Mobile App, has also been launched

Mera Aspataal

‘Mera Aspataal’
(My Hospital) IT-based feedback system collects information on patients’ level of satisfaction using a multi-channel approach viz. Short Message Service (SMS), Outbound Dialing (OBD), Web Portal, and Mobile Application. Under Phase I, more than
1000
hospitals have been covered and more than
14 lakh feedback
received so far.

Web-Portals

PMSMA Portal
supports Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan (PMSMA)

‘Hum Do’ Website
(www.humdo.nhp.gov.in) provides information and guidance on family planning methods.

Web-Portals

Mother and Child Tracking System (MCTS) / Reproductive Child Health (RCH) application:
Facilitates timely delivery of antenatal and postnatal care services and immunization to children. Approximately
14 crore
pregnant women and
12 crore
children registered on MCTS / RCH portal till date.

Kilkari
application delivers free weekly audio messages on pregnancy, childbirth and care. Approximately
10.58 crore
successful calls have been made.

Mobile Academy:
Free audio training course designed to expand and refresh the knowledge base of ASHAs and improve their communication skills. Launched in 2016, more than
1.11 Lakh
ASHAs registered in MCTS started the course.

ANM online (ANMOL)

ANM online (ANMOL)
allows ANMs to enter and update data for beneficiaries of their jurisdiction. Currently
11,941
ANMs in
Andhra Pradesh, 2,688
ANMs in
Telangana, 2,097
ANMs in
Madhya Pradesh
and
more than 362
ANMs in
Odisha
are using ANMOL.

Drugs and Vaccines Distribution Management System (DVDMS)
(‘e-Aushadhi’)
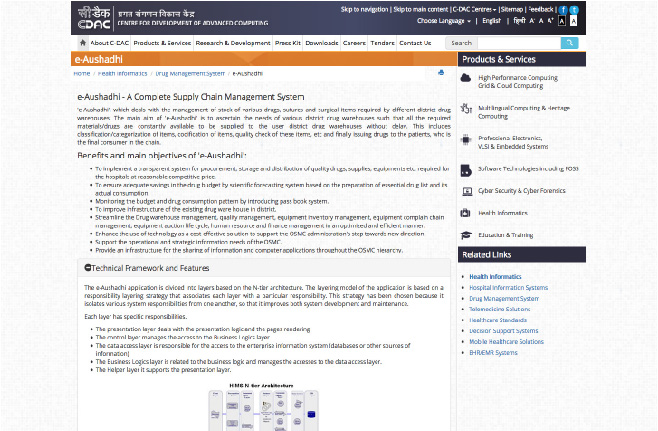
Drugs and Vaccines
Distribution Management
System (DVDMS)
(‘e-Aushadhi’):
For purchase,
inventory management and
distribution of various drugs,
sutures and surgical items
to various District Drug
Warehouses of State / UT,
District Hospitals (DH), their sub
stores at CHC, PHC etc.

TB Patient Monitoring System “Nikshay”

TB Patient Monitoring System “Nikshay”:
A
web-based solution for
monitoring of TB patients.
About
72 lakh patients
registered.
A Missed Call
Centre facility with Toll-
Free No: 1800-11-6666
reaches the unreached TB
patients, for counselling
and treatment support.

SUGAM

SUGAM
by Central Drugs
Standards Control Organisation
(CDSCO) enables online submission
of applications, their tracking,
processing & grant of approvals
online, mainly for drugs, clinical trials,
ethics committee, medical devices,
vaccines and cosmetics.

eRakt Kosh
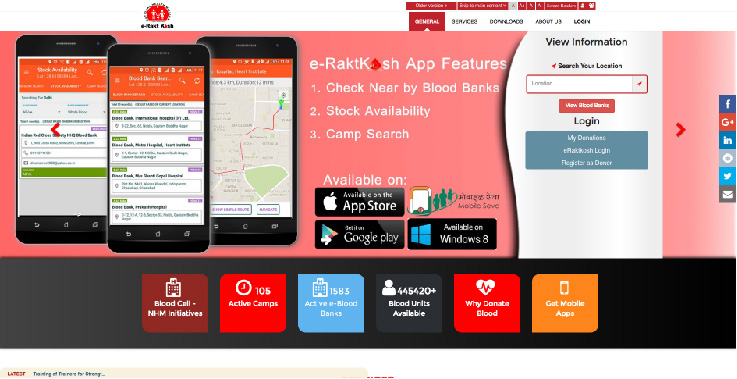
eRakt Kosh
being rolled out for all
the licensed blood banks in public
and private health facilities.
1360
active blood banks
on network till
date. Mobile App also available.





. Indradhanush Immunization
For immunisation tracker
. India Fights Dengue
Enables a user to check Dengue Symptoms,
get nearest Hospital / Blood bank information
and also share feedback
. NHP Swasth Bharat
Information dissemination on Disease,
Lifestyle, First Aid
. NHP Directory Services Mobile App
Information related to Hospital and Blood
banks across India have been hosted

• No More Tension Mobile App
Information on stress-management related aspects
• Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan Mobile App
For reporting pregnancy care related information from
across states
• NHP Health Information Kiosks
Have been installed in
17 hospitals
for the
dissemination of authentic health-related information to
the citizens through the touch screen based kiosks.


• Tobacco Cessation Programme
Is a mobile-based interventional initiative for
counselling and helping people to quit tobacco, by
giving a missed call to
011-22901701.
Currently,
over
20 lakh
total missed calls have been
captured and more than 14 lakh users registered.
• mDiabetes Program
Is a mobile-based initiative for prevention and
care of diabetes by giving a missed call to
011-22901701.
Currently, more than
1 lakh
users
are registered for diabetes




EHR Standards
Revised version of 2013 Standards
notified in December 2016. Includes
standards for Disease Classification
Medicine and Clinical terminology,
Laboratory Data exchange, Digital
Imaging and Communication etc.,
for semantic interoperability.


Metadata and Data Standards (MDDS) for Health
Is to enable semantic interoperability among healthcare
applications. The MDDS standards have
more than 1000 data
elements to be used in healthcare applications and are aligned
with the global health IT standards.



National Resource Centre for EHR
Standards (NRCeS)
Augments facilitation for adoption of
the notified EHR Standards in technical
association with C-DAC, Pune for
providing assistance in developing,
implementing and using EHR standards
effectively.


National Digital Health Authority (NDHA)
Is a nodal agency for formulation, adoption & regulation
of eHealth Standards in India as well as to develop
a regulatory framework for the Privacy and Security
aspects of digital health records.


National Identification Number (NIN)
A unique identification number is being assigned to all health
facilities (both public & private) to facilitate interoperability
among health IT systems deployed. So far
approximately 99%
of Public Health Facilities allocated NIN.


Hospital Information System (HIS)
Was implemented for computerized registration and capturing EHR/ EMR of
patients in Public Health facilities up to PHC level. So far,
financial assistance
provided to 18 States/UTs
for implementation of HIS application like
eHospital (NIC),e- Sushrut (C-DAC Noida) etc.


Online Registration System (ORS)
Links various hospitals for online registration, payment of fees and
appointment, online diagnostic reports, inquiring availability of blood
etc.
More than 140 hospitals
are on board and around
13 lakh
appointments have been transacted online.


Electronic Vaccine Intelligence Network (eVIN)
Indigenously developed technology system that provides
real-time information on vaccine stocks and flows, and storage
temperatures across all cold chain points through a smartphone
application. Implemented across
19 states & 2 UTs.



National Medical College Network (NMCN)
50 Government Medical Colleges
being interconnected for e-Education and
e-Healthcare delivery, riding over NKN (National Knowledge Network). National
Resource Centres (NRC) with required centralised infrastructure and
7 Regional
Resource Centres (RRCs)
have been established.


State Telemedicine Network (STN)
will provide Telemedicine Services to
the remote areas by upgrading existing Government Healthcare Facilities
in States. Ten states have been financially supported in the last two years.


Telemedicine Nodes at pilgrim places
uses space technology for
telemedicine facility between identified remote patient-end health facility
and specialty hospital in collaboration with Department of Space.


JIPMER-BIMSTEC
To improve regional cooperation by strengthening telemedicine-
based patient care services and share medical knowledge among the
Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic
Cooperation (BIMSTEC) Countries.


Tele-Evidence
Doctors can testify in the judicial process utilizing the video conferencing
facility without visiting the courts. Operational in PGIMER, Chandigarh since
March 2014.
More than 4000 Summon Cases attended till date.







