From Data to Diagnosis
Transforming Healthcare through Digitalization
Introduction
India's healthcare landscape is undergoing a digital transformation, driven by government initiatives, policy reforms, and technological advancements. With a rapidly growing population and increasing demand for quality healthcare, digital health solutions are playing a crucial role in enhancing accessibility, affordability, and efficiency. Digital healthcare infrastructure in India is evolving to bridge the gap between urban and rural healthcare services, leveraging telemedicine, electronic health records (EHRs), and artificial intelligence (AI)-driven diagnostics.
The recent World Economic Forum (WEF) article highlights India's potential to become a global leader in digital health by building a resilient digital health ecosystem. The report emphasizes the role of public-private partnerships, the importance of interoperability, and the need for robust data governance frameworks. It underscores how India’s initiatives, such as the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) and the Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS), can set a global benchmark for digital healthcare transformation.
The World Economic Forum Article on India's Digital Health Potential

The WEF article, "India Can Be a Global Pathfinder in Digital Health," released on 15 January 2024, explores how India's digital healthcare initiatives position the country as a leader in health technology. Key takeaways from the report include:
- Interoperability and Standardization: Ensuring seamless data exchange between stakeholders.
- Public-Private Collaboration: Encouraging partnerships for innovation and expansion.
- Focus on Affordability and Accessibility: Leveraging digital tools to make healthcare inclusive.
- Global Influence: India’s digital health models could serve as templates for other developing nations.
The article acknowledges that India's digital health strategies can contribute to global health equity, improving healthcare outcomes across diverse populations. The article further acknowledges India's proactive approach to digital health, characterized by its robust digital public infrastructure and innovative private sector, positions the nation as a global leader in developing adaptable healthcare solutions. The World Economic Forum's Digital Healthcare Transformation (DHT) Initiative acknowledges India's potential to create scalable models that can be adopted worldwide, emphasizing the importance of cross-border collaboration in addressing universal healthcare challenges. This recognition underscores India's commitment to leveraging technology for equitable and efficient healthcare delivery, setting a benchmark for other nations to follow.
Digital Healthcare Infrastructure
1. Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM)

The ABDM aims to create a nationwide digital health ecosystem by integrating healthcare service providers and patients through unique health IDs. The objective of the scheme is to fill critical gaps in health infrastructure, surveillance and health research – spanning both the urban and rural areas so that the communities are Atma Nirbhar in managing such pandemic/ health crisis. Key features of ABDM include:
- Health ID: A unique identifier for individuals to store and share medical records.
- Healthcare Professionals Registry (HPR): A comprehensive database of registered healthcare professionals.
- Health Facility Registry (HFR): A digital repository of healthcare facilities across India.
- Unified Health Interface (UHI): An open network facilitating digital health services.
Over two lakh Ayushman Arogya Mandirs have been established across the country to facilitate early diagnosis and treatment. These Arogya Mandirs enable crores of citizens to easily check for diseases like cancer, hypertension, and diabetes.
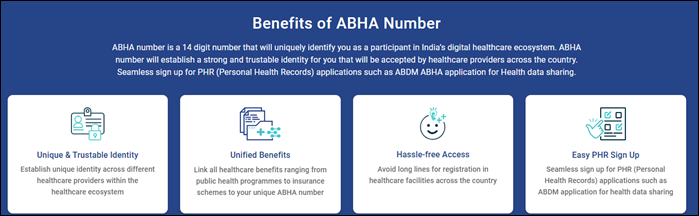
The Mission, further, provides for assisted and offline mode for creation of Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA) for areas with limited internet connectivity or hardware or both. As on January 20, 2025, more than 73 crore Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA) have been created successfully and there are more than 5 lakh health professionals registered. Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat are the top 5 states with Ayushman Bharat account holders. 49.15% of the total number of beneficiaries are women.
Recently, in September 2024, the National Health Authority (NHA) and IIT Kanpur signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), under which a federated learning platform across a variety of machine learning model pipelines, a quality-preserving database, an open benchmarking platform for comparing & validating AI models, and a consent management system for research under ABDM would be developed by IIT Kanpur. The platform will subsequently be operated and governed by NHA, thereby unlocking the immense potential of AI for improving health outcomes.
Introduced under ABDM, the Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS) encourages healthcare providers to adopt digital health solutions by offering financial incentives for integrating digital health records and services. The scheme incentivizes hospitals, clinics, and healthcare startups to embrace digital technologies, accelerating the transition to a paperless healthcare system.
2. Telemedicine and e-Sanjeevani
\






 स्वास्थ्य एवं परिवार कल्याण मंत्रालय
स्वास्थ्य एवं परिवार कल्याण मंत्रालय 





























